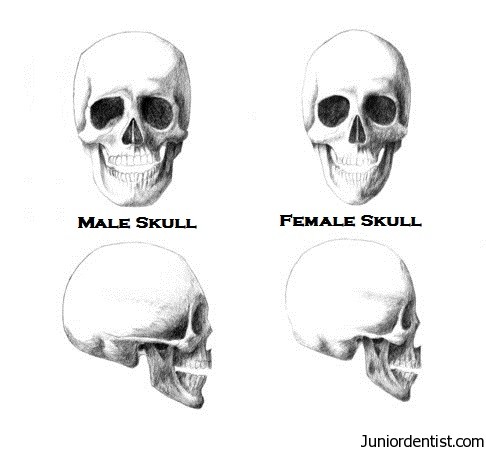
Differences between male and female skull are very important in forensics to determine the sex of the skull which has been recovered. From our ancestors, the differences in the skulls of males and females have been similar in obtaining different characteristics, which will be explained in the post below. The most obvious difference is the size of the skull but that depends on many factors like age, ethnicity, race, etc. The Differences between male and female skulls play an important role in Forensic odontology as well to help the police in their investigations.
We can look at many aspects to come to a conclusion, like weight of the skull, size, mandible. . .etc.
Weight:
- Male: Heavier
- Female: Lighter
Size:
- Male: In males, the skull size is larger than that in females.
- Females: Smaller compared to that in males.
The bony mass or the thickness of the bone:
- Males: Thicker
- Females: Thinner
Forehead:
- Males: In males, the forehead is slightly sloping or receding.
- Females: The forehead is vertical.
Vault of the skull:
- Males: The vault of the skull is more rounded.
- Females: The vault is flattened than that in females.
Contour of the face:
- Males: The overall length of the skull is longer and the chin is bigger and protrudes more forwards, the skull is rugged due to its muscular make up, and the zygomatic bones are also more massive.
- Females: The skull is Rounded, with the facial bones being more smoother, with both the jaws mandible and the maxilla being smaller.
Supraorbital margin:
- Males: More rounded
- Females: Sharp.
Tympanic plate:
- Males: Larger and the margins are rounded.
- Females: Smaller and the margins are less rounded.
Frontal bone and Forehead:
- Males: Brow Ridges are well demarcated
- Females: Smooth more vertical Frontal bone
Mastoid Process:
- Males: Large Mastoid process
- Females: Small Mastoid process
These differences are very important in determining the sex of a skull in Forensic Dentistry or Medicine.
But if you are interested to do your own research start digging in your back yard, who knows you might get a pair of skulls so just look at these features to know wether it is of a male or female.

approximate male skull size in inches/meters, esp. back view
Helloo, you’ve a great blog. I like it!
Thanks for all that information.
orbits are square in males.
If you found a skull in your backyard surely you wouldn’t touch it and wonder how it got there in the first place!:/
what is the difference between male and female jaw?
Male Jaws have sharp edges and the female jaw bones are rounded at the Angle of the Jaw – Main difference The Female Jaws are smaller than Male Jaw’s both Maxilla and Mandible.
This is a very good reseach it has helped me in soo many ways and has also brightend my idea about skull.
Sexing skull is one of the least credible ways of determining sex of an individual. No model for cranium exceeds 90%.
Good, now can someone explain this to ‘Michelle’ Obama?
Gud. Help a lot in medical research and for my seminar too
Interesting love.it.and.thanks
Now my boyfriend will stop arguing with me about this. I tell him all the time that to identify a male and a female we use the skull. Thanks a lot for this info :) just showed him your website.
But if I have one skull how can I know if is male or female skull with out comparison
Forehead shape (Vertical – females and sloping – males), size of mastoid process can be a good indication for identifying the skull individually.
would you,please, kindly send this article and others to my mail address? thanks.
Great! But what is the biological significant to these differences? Why are they different?
One major thing is Evolution, the priorities of men and women have changed over time. This can be seen with the decrease in the size of Jaw leading to increased Impactions or third molars.
Thanks alot.this differences has eazy my studies this semester.big ups
So it looks like those famous tennis sisters really are men after all!
haha that is some assumption from this post.
This is so transphobic.
THIS IS VERY HELPFUL FOR ME HOW TO DISCRIMINATE THE MALE AND FEMALE X-RAY . THANKS FOR THIS ARTICLE
I have went to many sites and some say the female skull is bigger then the male skull. I need help to understand if that is correct or false?
Female Skull is smaller than the Male skull in almost all aspects. You can refer to certain Archeological journals as well for confirmation. The Mastoid process, the Mandible etc are all larger in size in Males as compared to Females.
The female jaw, without exogenous testosterone influence, subtly curves (a very subtle curve, not “rounded”) directly from the earlobe to the chin, with a shorter overhang over the front neck, with connective tissue joining the neck to the underside of the lower jaw, with a pointy-rounded and longer chin, the frontal view being that the lower face is visibly tapered from the temporal lobes and cheekbones down to the narrowed chin. The female jaw, without exogenous testosterone influence, is narrow, having a narrow dental arch with small teeth, with less space between the upper lip and the bottom of the nose. The male jaw, without exogenous estrogenic influence, drops straight down from the earlobe, by about an inch and a half, then comes forward razor flat all the way to the square male chin, has a significantly longer overhang, with No connective tissue draping from the lower jaw to the neck, very clean of extra tissue under the lower jaw. The male jaw is wide, having a large wide dental arch of large teeth, big mouth, with a protruding (forward) square chin. From the front, the male jaw is wide, squared, not vertical, with the jaws being nearly as wide as the high wide cheekbones. These clear markers are made ambiguous when exogenous hormones are imposed in early development, but proof markers are still visible. Exogenous testosterone can cause testosterone jowls in FTM ‘s, that appear to make the jaw look wide from the front, but the bones do not bear that out. Jowls can be deceptive. The bones tell the tale. Without exogenous testosterone influence, the female jaw and head is shallower, shorter in all directions, while the male, without exogenous estrogenic influence, jaw and head is longer, wider in all directions.
The male brain is larger, thus the male skull is larger as well, with a high male crown of head, while the female skull is smaller, shorter in every direction, shorter in length and depth and width, with a low female crown of head, as the shallower skull rounds down much sooner on the top rear of a natural female head. There are lies and liars that want to create confusion about the differences between the genders forensics. Everything about the natural male is bigger, bones, head, jaw, musculature, ankles, wrists, neck, and don’t forget, the high male crown. The male skull, jaw is boxy, while the natural female is small, smooth, with a heart-shaped face. A female will have a short torso and long legs, while the natural male has a torso equal in length from the top of the very square 3X shoulders to the groin, as the length of his legs. Exogenous hormones can cause these ratios to develop falsely, creating a lie, but the spinal curve is hard to develop falsely. Cis-females have a spinal curve, forming an S shape, when viewed from the right side, with a deep small of the back, followed by a shapely and protruding derriere, while the male has a relatively flat backside, a flat back. Females have sloping narrower shoulders with a shorter, slender neck. The hands are also very different, bony and muscular and squared on the male, smooth and triangular on the female without any base of thumb knuckle protrusion. In like manner, male feet are also wide, squared, while female forefeet are tapered with a narrow heel.
The male brain is larger, thus the male skull is larger as well, with a high male crown of head, while the female skull is smaller, shorter in every direction, shorter in length and depth and width, with a low female crown of head, as the shallower skull rounds down much sooner on the top rear of a natural female head. There are lies and liars that want to create confusion about the differences between the genders forensics. Everything about the natural male is bigger, bones, head, jaw, musculature, ankles, wrists, neck, and don’t forget, the high male crown. The male skull, jaw is boxy, while the natural female is small, smooth, with a heart-shaped face. A female will have a short torso and long legs, while the natural male has a torso equal in length from the top of the very square 3X shoulders to the groin, equal to the length of his legs > a very long torso, shorter legs. Exogenous hormones from early childhood can cause these ratios to develop like the opposite gender, but the spinal curve is hard to develop falsely. Cis-females have a spinal curve, forming an S shape, when viewed from the right side, with a deep small of the back, followed by a shapely and protruding derriere, while the cis-male has a relatively flat backside, a flat back, no deep small of the back, no shapely tush. Females have sloping narrower shoulders with a shorter, slender neck, and very mild musculature. The hands are also very different, bony and muscular and squared on the male, smooth and triangular on the female without any protrusion of the base-of-thumb knuckle. In like manner, male feet are also wide, squared, with the big toe base knuckle protruding very visibly, while female forefeet are gently shaped, tapered with a narrow heel. So too with the back of the heel, the Achilles tendon area, where a sandal strap would be, as the male heel comes straight down, and the female heel curves gently inward, coming back out to the base of the heel. The biggest proof markers are the size of the head, the shape, the high male crown versus the low female crown, the jaw structure, the length of the neck, the shoulders, the trachea Adam’s apple area, as there will be no tracheal cording visible on a cis-female, the length of arms, the torso to leg length ratio, the spinal curve or lack thereof, the joints of the hands and feet, the dental arch and size of teeth, the size and placement of eyes, female eyes being moderate in size and closer together. Opposites abound, while authenticity is rare.
CA’s description of skeletal differences are fairly accurate. Certain skeletal features are formed within the first trimester. It is the presence of testosterone that makes masculine changes happen, also called virilization of the fetus. With regards to the spinal curve, this is created by the formation of the sacroliliac joint profile. With testosterone this forms into a longer more vertical joint profile. Without testosterone this forms a shorter joint with the sacrum angled as much as 20 degrees more reward from the vertical. The ilium bones are often also much more flared outward and form the basis of the wider pelvis in females later in life. Another testosterone based change is the angle of the knee and elbow joint profiles. The knees being much more visible even before puberty begins.
Very helpful, especially for school projects!
What are your sources? What research are you referencing? If you have any reliable sources, why don’t you post them hmmmmm?
My man came 13 years later to defend their political agenda to post about evidence you could acquire yourself irl. You cant possibly believe there aren’t skeletal differences in the average male and average female.
Why do famous people have opposite skulls? The women actressess have male skulls and the men have female skulls.????
Is it ?? Any sources you would like to share. This surely is interesting if true.